Nerve Cell Communication Answer Key
Glial cells are non-neuronal cells that provide support and nutrition maintain homeostasis form myelin and facilitate signal transmission in the nervous system. Each segment of the spinal cord is associated with a pair of ganglia called dorsal root ganglia which are situated just outside of the spinal cord and contain cell bodies of sensory neurons.
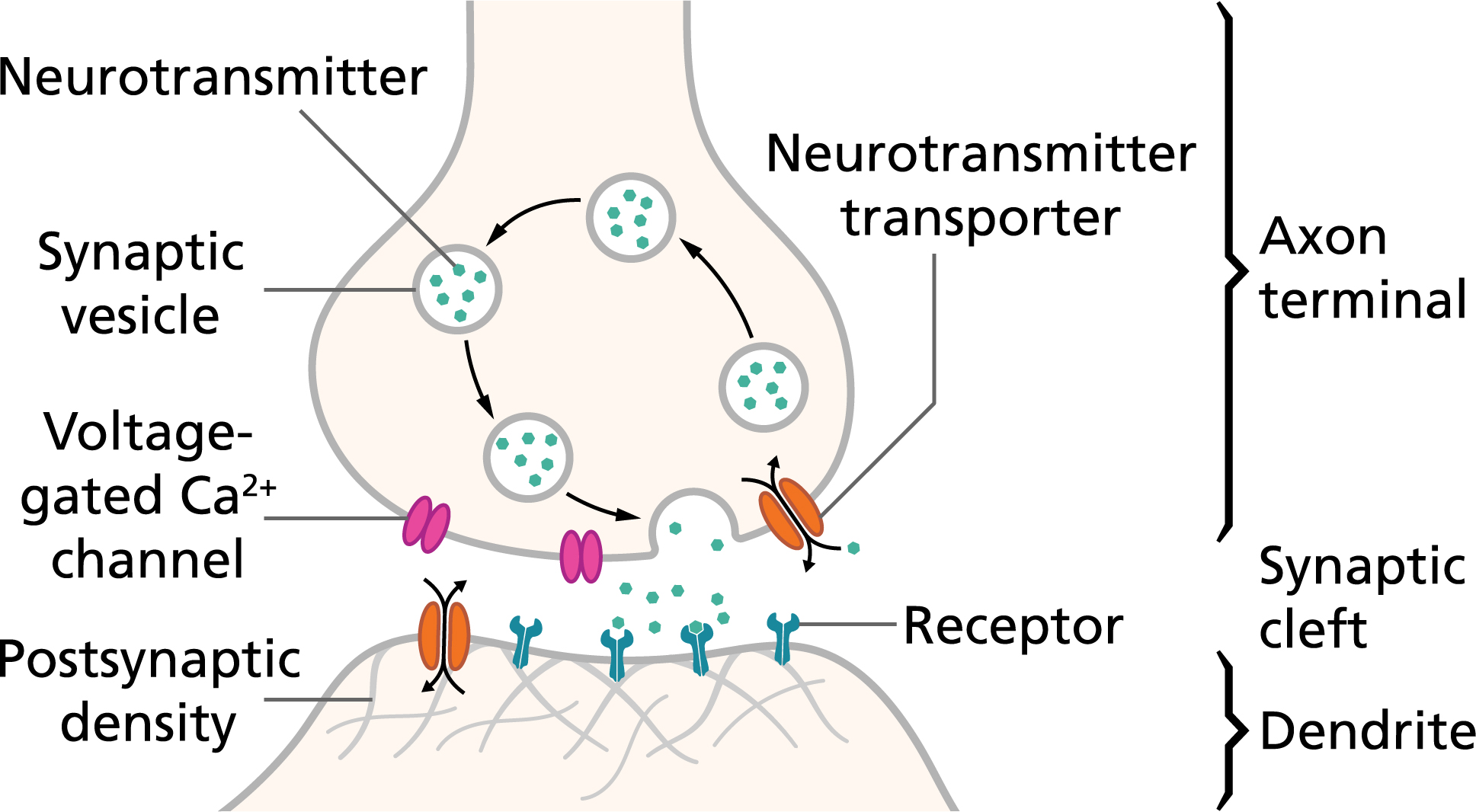
Action Potentials And Synapses Queensland Brain Institute University Of Queensland
A receptor is a molecule that receives signals chemical or hormonal from outside the cell and is usually located on the cell surface.
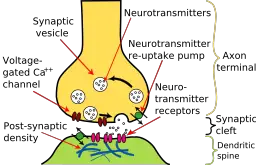
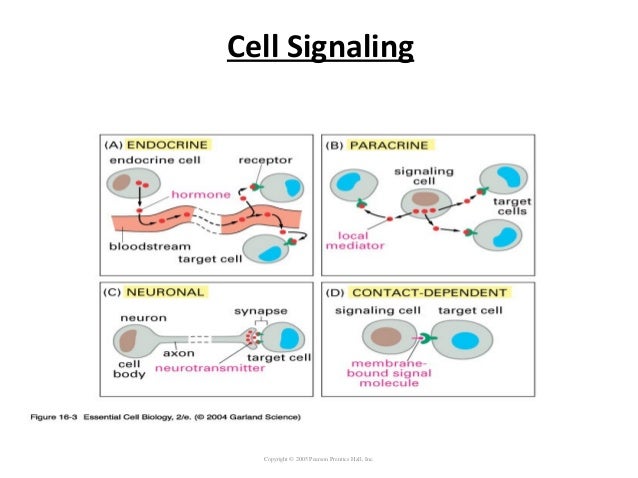
Nerve cell communication answer key. Blood cell functions include - releasing oxygen binding carbon dioxide and eliminating waste. Cell of the nervous system that conducts nerve impulses. Such a differentiated system calls for a long-distance communication between the axon terminals which are in contact with epithelial or muscle cells and the cell bodies in the ganglia. Neurons are specialized to pass signals to individual target cells and synapses are the means by which. Synapses are essential to the transmission of nervous impulses from one neuron to another. In the nervous system a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron or nerve cell to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell.
The internal auditory meatus is approximately 1. Consisting of an axon and several dendrites. Because it plays a key role in maintaining the survival of. They maintain homeostasis form myelin in the peripheral nervous system and provide support and protection for neurons. After exiting the cerebellopontine angle see Figure 1 the two facial nerve roots are seen as a larger medial motor root and smaller lateral sensory root. Cell in the nervous system that supports and protects neurons.
These two nerve roots travel ventro-laterally together to enter the internal auditory meatus on the posterior aspect of the petrous temporal bone. The brain is made up of two types of cells. The Schwann cell a glial cell forms a myelin sheath enclosing an axon of a peripheral neuron which play a role as an insulator of axon fiber. Glia also called glial cells singular gliocyte or neuroglia are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system brain and spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. In the central nervous system glial cells. The neuron is responsible for sending and receiving nerve impulses or signals.
It helps your heartbeat stay regular. Neurons and glial cells also known as neuroglia or glia. The forearm vein most commonly used for venipuncture is the -. The intracranial facial nerve. Permission granted by a person voluntarily and in his right mind is - consent. Palmitoylethanolamide PEA belong to endocannabinoid family a group of fatty acid amides.
Receptors are proteins that undergo a conformational change upon attachment of their corresponding signaling molecule which in turn induces a chain reaction also known as signal transduction within the cell leading to various. The spinal cord is divided into 31 segments that send nerve rootlets out into the body through intervertebral foramen. As the vestibular schwannoma grows it affects the hearing and balance nerves usually causing unilateral one-sided or asymmetric hearing loss tinnitus ringing in the ear and. PEA has been proven to have analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity and has been used in several controlled studies focused on the management of chronic pain among adult patients with different underlying clinical conditions. An organ system that coordinates the bodys voluntary and involuntary actions and transmits signals between different parts of the body. It is a type of electrolyteIt helps your nerves to function and muscles to contract.
The tumor comes from an overproduction of Schwann cellsthe cells that normally wrap around nerve fibers like onion skin to help support and insulate nerves. The myelin sheaths form a spiral-like structure surrounding axons and are essential for the survival of neurons Bhatheja and Field 2006. Potassium is a mineral that your body needs to work properly. It also helps move nutrients into cells and waste products out of cells. The answer may lie within the specialized signaling and gene expression patterns that maintain highly polarized morphology and function of neurons.

Introduction To Cell Signaling Article Khan Academy Khan Academy Stem Lesson Cell
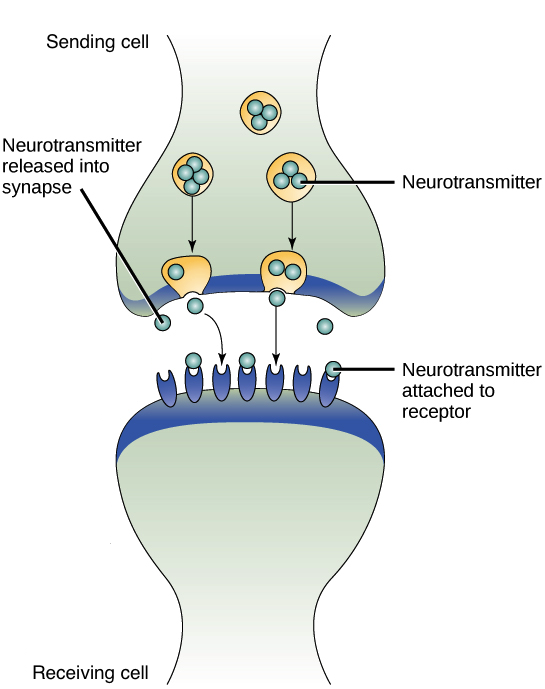
Introduction To Cell Signaling Article Khan Academy

Visualizing Dynamics Of Cell Signaling In Vivo With A Phase Separation Based Kinase Reporter Molecular Cell

Cell Cell Communication Enhances The Capacity Of Cell Ensembles To Sense Shallow Gradients During Morphogenesis Pnas

Q 2 Make A Sketch Of The Human Lido
Nerve Cells And Nerve Impulses

What Is The Length Of A Nerve Cell An Overview Of Nerve Cell

Pancreatic B Cells Communicate With Vagal Sensory Neurons Gastroenterology

Nerve Cells Neurons Structure Function Adaptations Microcopy
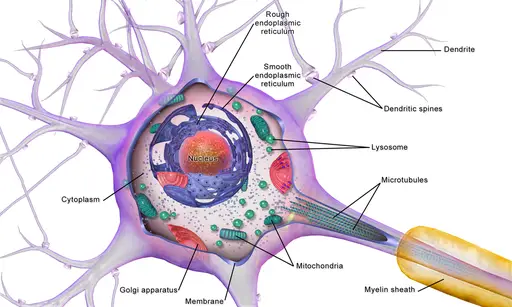
Nerve Cells Neurons Structure Function Adaptations Microcopy
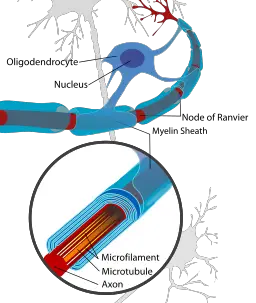
Nerve Cells Neurons Structure Function Adaptations Microcopy
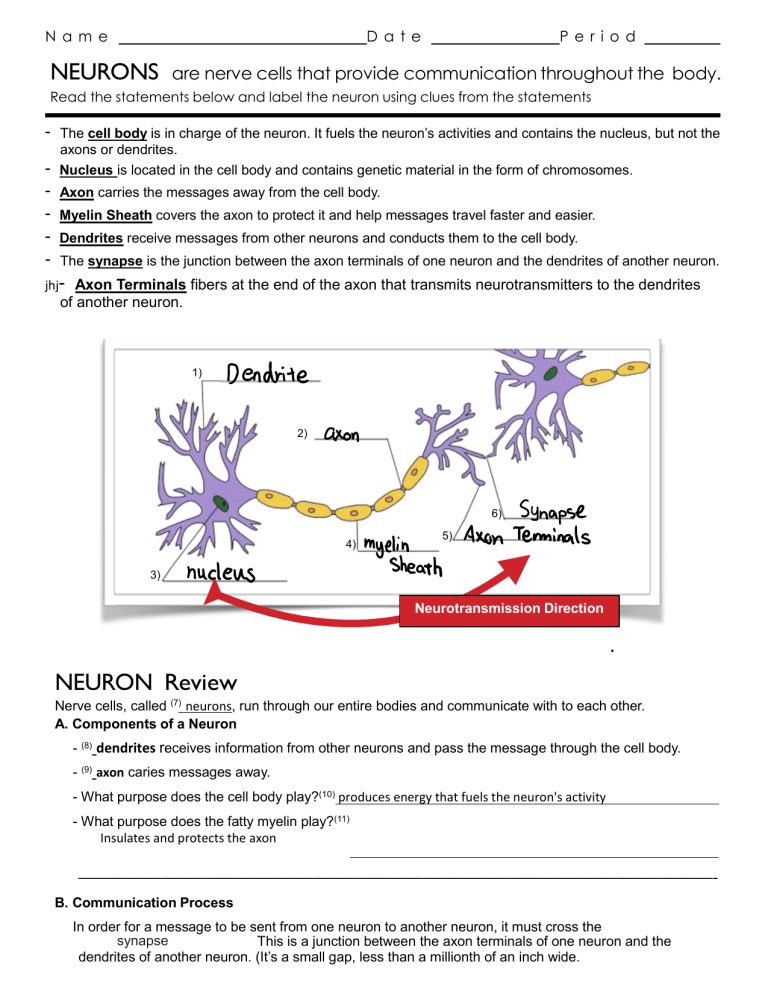
Posting Komentar untuk "Nerve Cell Communication Answer Key"