Differential Diagnosis Of T2 Hyperintense Spinal Cord Lesions
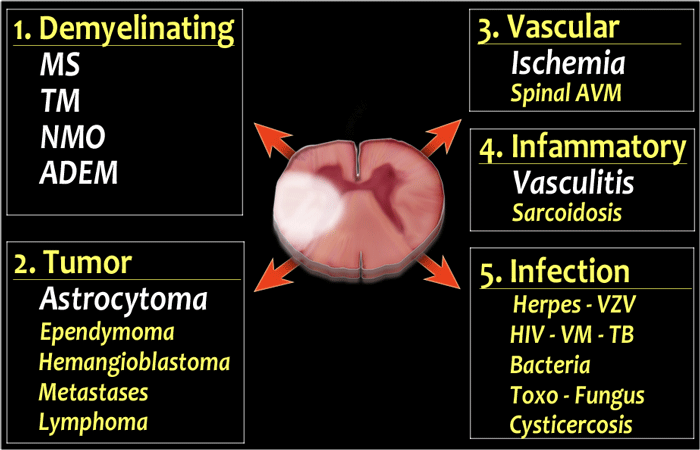
Differential diagnosis of T2 hyperintense spinal cord lesions. Tumor The major differential of demyelinating diseases is an astrocytoma especially if there is swelling and some enhancement of the cord and when the symptoms are.
Diffuse brainstem lesions are poorly defined often large abnormalities and include tumors gliomas and lymphomas vasculitis Behçets disease traumatic brainstem injury degenerative disorders Wallerian degeneration infections processes secondary to systemic.

Differential diagnosis of t2 hyperintense spinal cord lesions. Part B Differential diagnosis of T2 hyperintense spinal cord lesions. Discuss risks and benefits with a doctor. 4-6 They are typically T2 hyperintense relative to the spinal cord 56 although in the single largest review of spinal ependymomas isointense tumors were equally common. The authors present an algorithmic approach to evaluating. Causes including simple MR artefacts trauma primary and secondary tumours radiation myelitis and diastematomyelia were discussed in Part A. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol.
Simple MR artefacts congenital anomalies and most disease categories. Differential diagnosis of T2 hyperintense spinal cord lesions. If both halves of the cord are involved than think of Transverse Myelitis TM which is not a specific diagnosis but merely a reaction of the cord to various autoimmune and infectious stimuli. Lntramedullary Spinal Cord Lesions onMRImaging. InAandBarenotspecific forlupusmyelitisDifferential diagnosis includes other causesofmyelitissuchasherpessarcoidosis andimmune-mediated andidio-. Surfers myelopathy should be considered in the radiographic differential diagnosis of a longitudinally extensive T2-hyperintense spinal cord lesion.
Ad Watch Spinal Cord Stimulation patient testimonial videos on how SCS has impacted life. Segment length involvement is a very important distinguishing factor in spinal vascular lesions. Radiologists play a valuable role in helping narrow the differential diagnosis by integrating patient history and laboratory test results with key imaging characteristics. Up to 10 cash back The most common differential diagnoses for single tumefactive demyelinating lesions are high-grade gliomas HGGs and primary CNS lymphomas PCSNLs which show similar imaging characteristics such as a tumefactive andor infiltrative aspect perilesional edema and heterogeneous gadolinium enhancement. T2-hyperintense foci on brain MR imaging. Characterization of the abnormal areas of T2 signal as well as their appearance on other MR imaging sequences when combined with clinical context.
Reversal of MRI abnormalities may occur following treatment. T2-hyperintense foci are one of the most frequent findings in cerebral magnetic resonance imaging MRI. Hyperintense spinal cord signal on T2-weighted images is seen in a wide-ranging variety of spinal cord processes. Hyperintense spinal cord signal on T2-weighted images is seen in a wide-ranging variety of spinal cord processes. Intramedullary cord hyperintensity at T2-weighted MRI is a common imaging feature of disease in the spinal cord but it is nonspecific. Hyperintense spinal cord signal on T2-weighted images is seen in a wide-ranging variety of spinal cord processes including.
Intramedullary cord hyperintensity at T2-weighted MRI is a common imaging feature of disease in the spinal cord but it is nonspecific. Pattern 3issignal hyperintensity onT2-weighted images without spinal cordcontrast enhancement Appendix. They can pose serious diagnostic problems which is reflected by their English name and abbreviation - UBOs Unidentified Bright Objects. Differential diagnosis of T2 hyperintense spinal cord lesions. The typical imaging feature in cases of spinal cord infarction is T2 hyperintensity in a vascular-specific territory1 most commonly an anterior pencil-like lesion on sagittal sequences and owlsnake-eye pattern of signal abnormality on axial sequences corresponding to the anterior horn cells which are the most vulnerable to ischaemia 5 6 An adjacent vertebral. Hear what life is like after SCS.
MRI of the spinal cord especially in the dorsal segments shows hyperintense discrete lesions in T2W images which enhance with gadolinium. Causes including simple MR artefacts trauma primary and secondary tumours radiation myelitis and diastematomyelia were discussed in Part A. Part B BouHaidar P. Long-segment cord T2 hyperintensity should raise the suspicion of a dAVF or spinal cord infarct while short segment involvement raises the possibility of a cavernoma or arteriovenous malformation. On brain MRI multifocal white matter lesions may be seen 16 and occasionally positive oligoclonal bands are detected in the CSF 17 mimicking MS. Differential diagnosis of T2 hyperintense spinal cord lesions.
Karunaratne N 2009-04-01 000000 Introduction Multiple sclerosis demyelination Multiple sclerosis MS is a primary demyelinating disorder of the central nervous system CNS characterized by. Differential Diagnosis of T2 Hyperintense Brainstem Lesions. An algorithmic diagnostic approach to evaluating T2 hyperintensity in the spinal cord at MRI can help radiologists narrow the differential diagnosis in patients with myelopathy. Most ependymomas are T1-iso- or hypointense relative to the spinal cord. 5 Tumor margins are usually sharp and T2-signal alterations correspond well with the enhancing solid tumor. When a patient has a first attack of demyelination the physician should not rush.
Multiple sclerosis by contrast tends to have short-segment T2 hyperintense lesions in the periphery of the spinal cord and usually has associated classic intracerebral white matter lesions see Fig. A common misconception is that any attack of CNS demyelination means a diagnosis of acute multiple sclerosis MS. Hyperintense spinal cord signal on T2-weighted images is seen in a wide-ranging variety of spinal cord processes. The topics discussed in Part B of this two part series include multiple sclerosis subacute.

Diagnostic Approach To Intrinsic Abnormality Of Spinal Cord Signal Intensity Radiographics

Low Thoracic And Lumbar Spine Mri Showing A Hyperintense Lesion In The Download Scientific Diagram

Diagnostic Approach To Intrinsic Abnormality Of Spinal Cord Signal Intensity Radiographics

Spinal Cord T2 Weighted Mri Shows A Hyperintense Lesion Extending From Download Scientific Diagram

A Sagittal T2 Weighted Magnetic Resonance Image Showing A Hyperintense Download Scientific Diagram

Left Hyperintense Intramedullary Lesion In T2 At The Level C3 C7 Download Scientific Diagram
The Radiology Assistant Myelopathy

Diagnostic Approach To Intrinsic Abnormality Of Spinal Cord Signal Intensity Radiographics

Diagnostic Approach To Intrinsic Abnormality Of Spinal Cord Signal Intensity Radiographics
Posting Komentar untuk "Differential Diagnosis Of T2 Hyperintense Spinal Cord Lesions"