Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Vasospasm Pathophysiology
Delayed cerebral ischaemia DCI is any neurological deterioration 1 hour that presumed due to ischemia and other causes excluded. If the vasospasm is significant called clinical vasospasm a patient may develop neurologic changes and even suffer an ischemic stroke.

Does Prevention Of Vasospasm In Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Improve Clinical Outcome Yes Stroke
ENOS endothelial nitric oxide synthetase ROS reactive oxygen species.

Subarachnoid hemorrhage vasospasm pathophysiology. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage SAH Subarachnoid hemorrhage is sudden bleeding into the subarachnoid space. The most common cause of spontaneous bleeding is a ruptured aneurysm. Cerebral vasospasm has traditionally been regarded as an important cause of delayed cerebral ischaemia DCI which occurs after aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage and often leads to cerebral infarction and poor neurological outcome. The primary symptom is a sudden severe headache. A subarachnoid hemorrhage is bleeding in the space between your brain and the surrounding membrane subarachnoid space. This narrowing can reduce blood flow.
The initial hemorrhage is fatal in 20-30 of patients. Accordingly massive subarachnoid haemorrhage 05 ml was induced in adult rats via direct injection into the cisterna magna. SAH occurs when blood is released into the subarachnoid space which surrounds the brain and spinal cord. Subarachnoid hemorrhage is sudden bleeding into the subarachnoid space. Discover the best treatment and prevention methods for a subarachnoid hemorrhage today. The headache is sometimes associated with nausea vomiting and a.
Inflammation and oxidative stress play a vital role in the pathophysiology of cerebral vasospasm. Subarachnoid hemorrhage has effects outside the brain. A vasospasm is the narrowing of the arteries caused by a persistent contraction of the blood vessels which is known as vasoconstriction. Blood close to the brain surface is an irritant and many complications of subarachnoid hemorrhage are due to the irritant effect of blood on the brain. When the vasospasm occurs in the brain it is often due to a subarachnoid hemorrhage after a cerebral aneurysm has ruptured. Responses include seizures vasospasm and confusion.
The peak period for development of vasospasm occurs between the 7th and 10th days after the aneurysm bleeds but may extend to 14 days or longer after the hemorrhage. However the most important triggers for the occurrence of vasospasm and DCI are the amount density and prolongation of clot and erythrocyte degradation products in the subarachnoid space. Vasospasm is one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage SAH. Apoptosis a relevant cause of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage also underline the etiology of cerebral vasospasm. Symptoms of SAH include severe headache nausea vomiting neck pain nuchal rigidity and photophobia. The most common cause of spontaneous bleeding is a ruptured aneurysm.
Delayed neurological deterioration DND is clinically detected neurological deterioration after stabilisation that is not due to re-bleeding may be due to multiple other causes. A Subarachnoid sub-uh-rack noid Hemorrhage SAH occurs when a blood vessel either on or inside the brain suddenly begins to leak blood. Although the pathophysiology of chronic cerebral vasospasm following subarachnoid haemorrhage SAH is still unclear it is certain that the amount of subarachnoid blood is predictive of the severity of cerebral vasospasm. Radiographic vasospasm usually develops between 5 and 15 days after the initial hemorrhage and is associated with clinically apparent delayed ischemic neurological deficits DID in one-third of patients. After subarachnoid hemorrhage a pathophysiological cascade leads to vasospasm. This blood settles into a space between the surface of the brain and the skull called the subarachnoid space.
Oblique view of left ICA injection from emergent DSA following acute deterioration on postsubarachnoid hemorrhage day 6 C demonstrates severe vasospasm solid red arrows with sausage appearance in A2 branch and diffuse vasospasm of its distal segments dashed red arrows of the left ACA with delayed arterial filling in the ACA territory compared to DSA. Pathophysiological processes following subarachnoid hemorrhage SAH present survivors of the initial bleeding with a high risk of morbidity and mortality during the course of the disease. Symptoms include sudden severe headache usually with loss or impairment of consciousness. Ad Discover these incredible treatments for a subarachnoid hemorrhage today. The pathophysiology and treatment of acute subarachnoid hemorrhage SAH are reviewed. Discover the Best Tests to Accurately Diagnose Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.
Vasospasm is dynamic narrowing of vessels due to a radiological diagnosis. Secondary vasospasm causing focal brain ischemia meningismus and hydrocephalus. However data from recent studies argue against a pure focus on vasospasm as the cause of delayed. As angiographic vasospasm is strongly associated with delayed cerebral ischemia DCI and clinical outcome clinical trials in the last few decades focused on prevention of these angiographic. The leaked blood may also settle into other areas o f the brain but it is the blood in. Symptoms include sudden severe headache usually with loss or impairment of consciousness.
Discover What Sets Mayo Clinic Apart. Cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage aSAH is a well-described phenomenon that is defined as narrowing of the large and medium-sized intracranial arteries.

Sign In Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Inflammation Mindfulness
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Pathogenesis Calgary Guide
View Of Management Of Cerebral Vasospasm Following Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage The Southwest Respiratory And Critical Care Chronicles

Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Stroke

Invasive Multimodal Neuromonitoring In Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A Systematic Review Stroke

Stroke Type Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Neurology Nursing Students

Pathophysiology Of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Early Brain Injury And Delayed Cerebral Ischemia Sciencedirect

Inflammation And Cerebral Vasospasm After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Semantic Scholar

Pdf Management Of Cerebral Vasospasm Following Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Semantic Scholar

Neurocognitive Outcomes After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Identifying Inflammatory Biomarkers Journal Of The Neurological Sciences

Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Clinical Findings Calgary Guide Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Hemorrhage Clinic

Early Pathophysiology Of Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Acute Haemorrhage Download Scientific Diagram
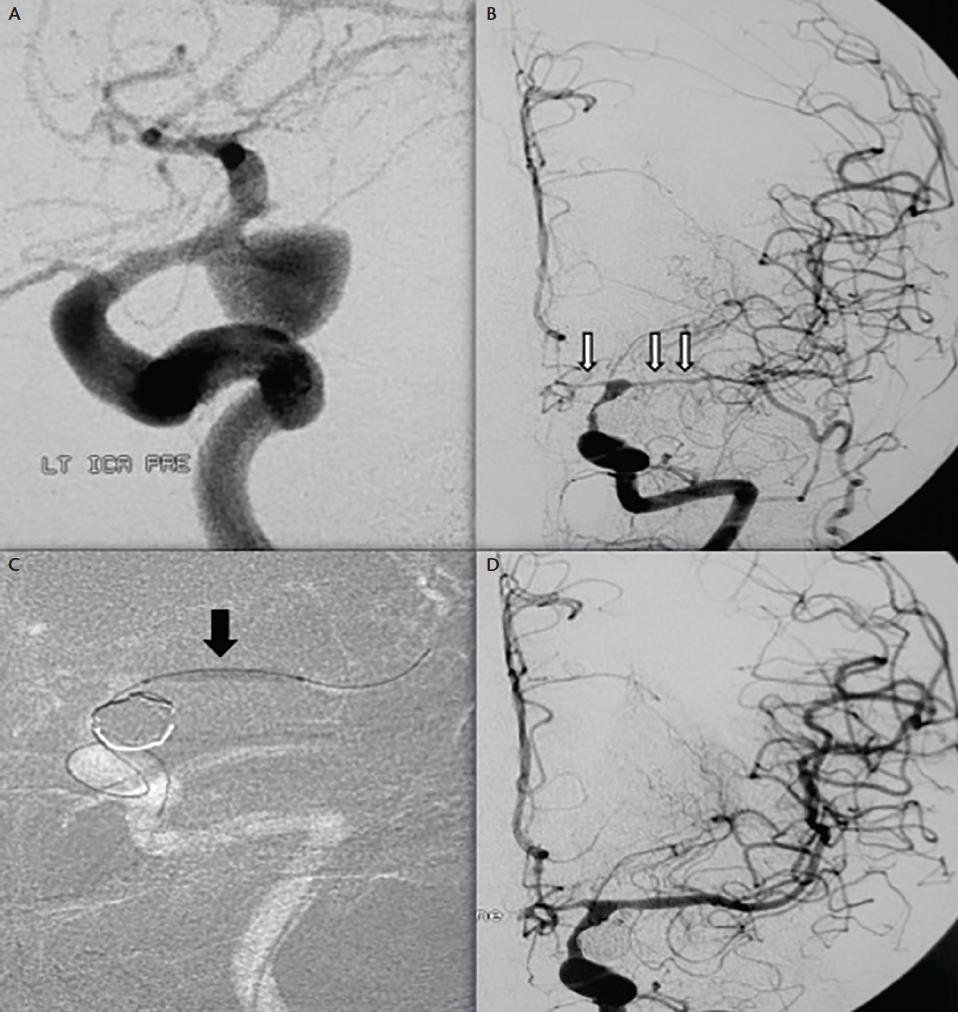
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Vasospasm And Delayed Cerebral Ischemia Practical Neurology
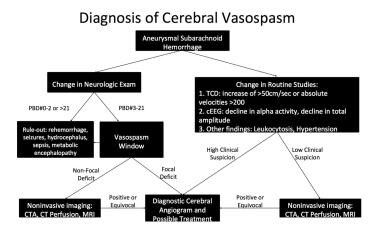
Cerebral Vasospasm After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Clinical Presentation History Physical Examination Complications
Posting Komentar untuk "Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Vasospasm Pathophysiology"