Chronic Infarct In Left Cerebellar Hemisphere
The Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation publishes original peer-reviewed research and clinical reports on important trends and developments in physical medicine and rehabilitation and related fieldsThis international journal brings researchers and clinicians authoritative information on the therapeutic utilization of physical behavioral and. 81 found reduced volumes in the left cerebellar hemisphere and right cerebellar vermis along with smaller volumes in.

Cerebellar Stroke Symptoms Treatment Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Ataxia is usually caused by cerebellar dysfunction or impaired vestibular or proprioceptive afferent input to the cerebellum.

Chronic infarct in left cerebellar hemisphere. Ng Leonid Churilov Nawaf Yassi Timothy J. Angiogram with selective injection of the right internal carotid artery demonstrates occlusion of the M1 segment of the right middle cerebral artery MCA and A2 segment of the. Vasculitis may affect large vessels Takayasu arteritis giant cell arteritis medium-sized vessels Kawasaki disease polyarteritis nodosa small vessels immunoglobulin A vasculitis. Chronic osteomyelitis with draining sinus ankle and foot M8648 Chronic osteomyelitis with draining sinus other sites M8649 Chronic osteomyelitis with draining sinus site unspecified M8650 Other chronic haematogenous osteomyelitis multiple sits M8651 Other chronic haematogenous osteomyelitis shoulder region M8652. Left Cerebellar Infarct Cytotoxic edema in infarctions involves the gray and white matter therefore abnormal low attenuation extends to the cortex Important to know vascular territories. 86-Year-Old Male With Leg Swelling After Hip Surgery.
TMoA is generally characterized by reduced speech output which is a result of dysfunction of the affected region. A 48-year-old man presented with acute left-sided hemiplegia facial palsy and right-sided gaze preference. Subdural hematomas may cause an increase in the. A and B CBV A and MTT B maps here shown in reverse color scheme obtained through the level of the posterior fossa show an area of ischemic penumbra in the right posterior inferior cerebellar artery territory arrows. 33-Year-Old Female Presents with Chronic SOB and Cough Case Study. CT SCAN Mandatory initial investigation Haemorrhage appears instantly as a hyperdense area Infarct appears as a hypodense area Infarct may not appear before 48 hrs MRI may be done instead but ct scan is more sensitive for detecting haemorrhage Diffusion weighted MRI is good for identifying ischaemic lesion.
His physical exam reveals bibasilar rales JVD of 5cm an S3 gallop a holosystolic murmur at the apex that radiates to the left axilla and 2 pitting edema to the level of the mid-calves bilaterally. Both the anterior and posterior lesions in the left hemisphere are known to produce apraxic symptoms as this is the dominant hemisphere for the storage and execution of learned movements Kareken 1998. The ICD-10-CM code I6389 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like cerebellar stroke syndrome cerebral infarction due to cerebral artery occlusion cerebral ischemic stroke due to aortic arch embolism cerebral ischemic stroke due to dissection of artery cerebral ischemic stroke due to global hypoperfusion with watershed infarct. 80 found significantly reduced vermis volume in neuroleptic-naive schizophrenic patients that correlated with the Depression and Paranoia subscores of the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale and Volz et al. Academiaedu is a platform for academics to share research papers. A middle cerebral CVA would result in greater effects in the face and upper extremities.
A posterior cerebral artery CVA would manifest with contralateral hemiplegia with possible dysmetria dyskinesia hemiballism or choreoathetosis dystaxia cerebellar ataxia and tremor. A bedside echocardiogram was remarkable for biventricular enlargement. Dewey Gargan Sharma Patricia M. A 48-year-old man presented with acute left-sided hemiplegia facial palsy and right-sided gaze preference. Transcortical motor aphasia TMoA also known as commissural dysphasia or white matter dysphasia results from damage in the anterior superior frontal lobe of the language-dominant hemisphere. Visual of the left side 12.
This is a posterior inferior cerebellar artery PICA infarct Acute to subacute stage of infarction can lead to mass effect from edema. The pathogenesis of vasculitis remains poorly understood. C DWI confirms a right lateral medullary infarct with salvage of the right inferior cerebellar hemisphere penumbra. Original studies showed that 50 of patients with rightsided hemiplegia suffered from motor apraxia Liepmann 1905. Cerebellar infarction is problematic due to the low volume of the posterior fossa. His psychosocial history is noteworthy for chronic alcohol use.
Hemineglect if in nondominant hemisphere usually right MCA territory Unawareness of and unresponsiveness to unilateral stimuli due to a brain unilateral injury most commonly strokes not due to a primary motor or sensory lesion Typically associated with right hemisphere damage resulting in neglect esp. Craniectomy for cerebellar infarct. An old left posterior parietal infarct is noted as well. The arachnoid membranes just inferior to the vein are sharply opened and additional cerebrospinal fluid CSF is released. Cerebral vasculitis is characterized by inflammation of the walls of blood vessels and may affect vessels of any size. Kleinig Vincent Thijs Teddy Y.
A rare chronic inflammatory disease that usually affects only one hemisphere of the brain. It occurs in children under the age of 10 and more rarely in adolescents and adults and is characterized by frequent and severe seizures loss of motor skills and speech paralysis on one side of the body hemiparesis inflammation of the brain. Similarly Ichimiya et al. Swelling may compress the brainstem or the cerebral aqueduct causing noncommunicating hydrocephalus. 60-Year-Old Female Presenting With Shortness of Breath Case Study. Angiogram with selective injection of the right internal carotid artery demonstrates occlusion of the M1 segment of the right middle cerebral artery MCA and A2 segment of the.
Cerebellar edema with clinical deterioration is generally regarded as an indication for suboccipital crainectomy. Gentle inferomedial retraction of the cerebellar hemisphere exposes the superior petrosal vein. We have observed behavioral and neuropsychological disorders acutely following cerebellar infarction. A subdural hematoma SDH is a type of bleeding in which a collection of bloodusually associated with a traumatic brain injurygathers between the inner layer of the dura mater and the arachnoid mater of the meninges surrounding the brainIt usually results from tears in bridging veins that cross the subdural space. Any of the following can be implicated in pathology. Neuropsychological testing was performed in a 64-year-old right-handed woman with an MRI-documented infarct in the territory of the left superior cerebellar artery.
And contralateral upper motor neuron palsy. An old left posterior parietal infarct is noted as well. This damage is typically due to cerebrovascular accident CVA. Microvascular Dysfunction in Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption and Hypoperfusion Within the Infarct Posttreatment Are Associated With Cerebral Edema. Academiaedu is a platform for academics to share research papers. Cerebellum spinal cord brain stem vestibular nuclei basal ganglia thalamic nuclei cerebral white matter cortex especially frontal and peripheral sensory nerves.
SPECT revealed crossed cerebello basal ganglia cortical diaschisis Botez-Marquard et al 1994. However the arachnoid membrane over the petrosal vein and CN VIIVIII are left intact to protect these structures.

Stroke Fact Sheet Stroke Awareness Fact Sheet Operating Room Nurse

There Are Several Mnemonics On Memorizing Signs Of Cerebellar Damage Here S One Out Of T Medical School Motivation Nursing Mnemonics Nurse Practitioner School

Mri T2 Coronal Left And Axial Right Views Of Cerebellar Infarction Download Scientific Diagram

Mri Head Shows Smaller Infarct Posterior To Left Cerebellar Hemisphere Download Scientific Diagram

T2 Weighted Mri Showing The Infarction In The Left Cerebellar Hemisphere Download Scientific Diagram

A E Left Superior Cerebellar Artery Occlusion Contrast Enhanced Ct Download Scientific Diagram

On Month 4 Mri Demonstrates A New 2 Cm Lesion In The Left Cerebellar Download Scientific Diagram
Remote Cerebellar Hemorrhage American Journal Of Neuroradiology
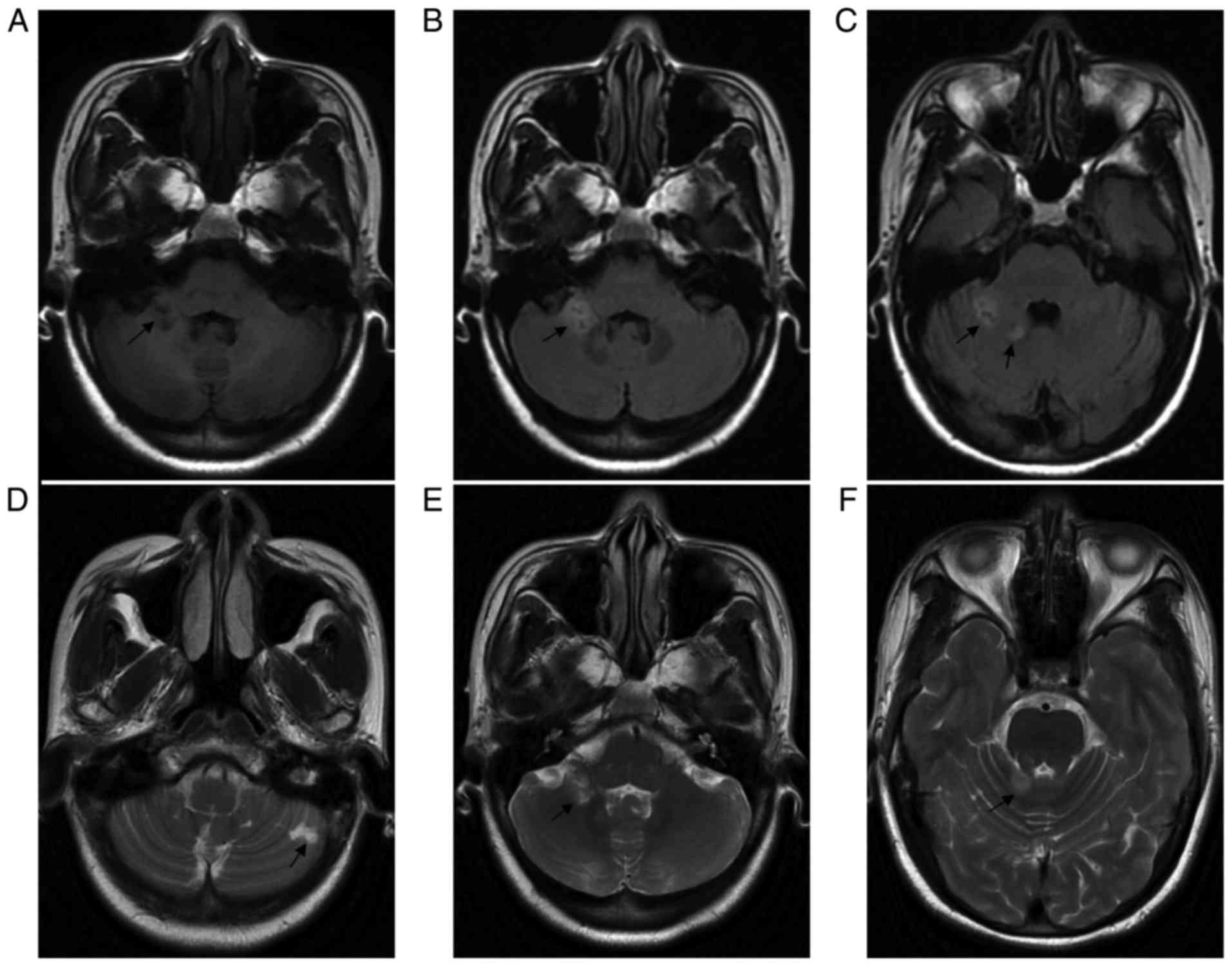
Recurrent Cerebellar Infarction Associated With Hereditary Heterozygous Protein C Deficiency In A 35 Year Old Woman A Case Report And Genetic Study On The Pedigree

Mri Head Shows Left Cerebellar Hemisphere Anteriorly Abutting Superior Download Scientific Diagram

Axial T2wi Show Multiple Chronic Infarcts In The Left Cerebellar Download Scientific Diagram
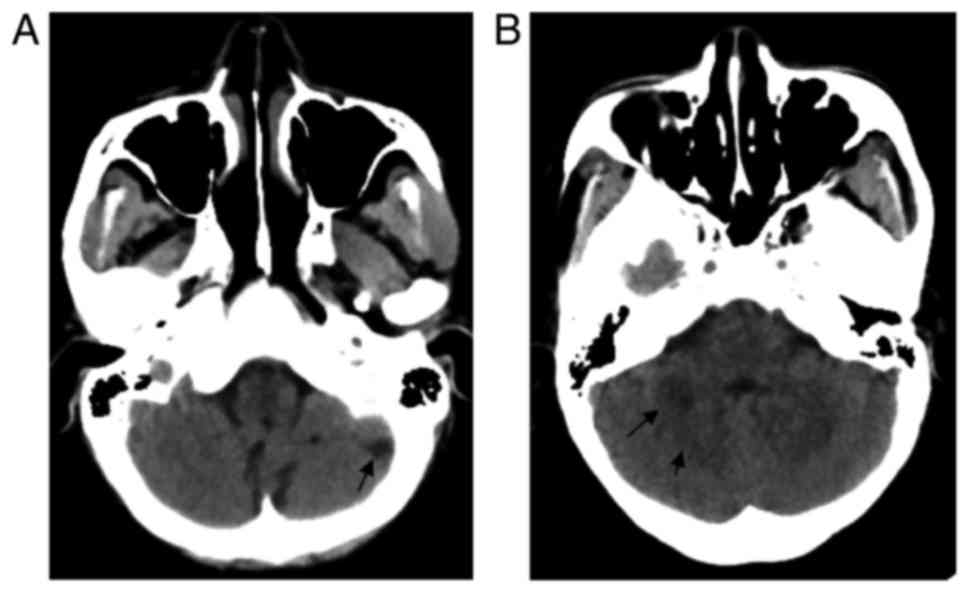
Recurrent Cerebellar Infarction Associated With Hereditary Heterozygous Protein C Deficiency In A 35 Year Old Woman A Case Report And Genetic Study On The Pedigree

Hyperacute Infarction 6 Hrs Hyperdense Mca Sign Mca Signs False Positive
Posting Komentar untuk "Chronic Infarct In Left Cerebellar Hemisphere"