Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Lesion Differential Diagnosis
Involvement of both middle cerebellar peduncles is uncommon but has a relatively long list of differential diagnoses including 1. Fragile X-associated tremorataxia syndrome.
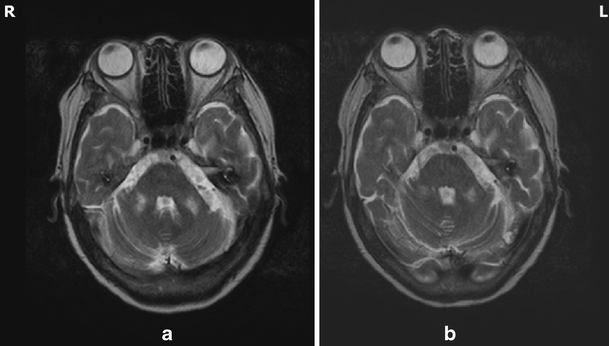
Ataxia And Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Lesions In Hepatic Encephalopathy Springerlink
METHODS MR findings of 27 patients 14 male and 13 female.

Middle cerebellar peduncle lesion differential diagnosis. Pontine grey lesions cause hemiparesis and ataxia of the contralateral side. At this time the patient has. The middle peduncle is purely afferent. Age range 4-77 years. Bilateral middle cerebellar peduncle lesions. It also contains the bilaterally projecting fibers from the nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis.
The middle cerebellar peduncle MCP consists of. Lesions in the middle cerebellar peduncle include various pathological conditions ranging from infarction tumor infection trauma and demyelination to primary and secondary degeneration. The purpose of this paper is to show several diseases that manifest symmetrical hyperintense lesions on the middle cerebellar peduncles the largest connecting peduncles between the brainstem and the cerebellum in conventional magnetic resonance MR images. Lateral surface of the brainstem Lateral. The middle cerebellar peduncle or the brachium pontis enters the cerebellum fairly laterally. Axial FLAIR sequence B showing hyperintensity in bilateral middle cerebellar peduncles with pontocerebellar atrophy.
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE Distribution of lesions or involvement of specific anatomic sites can suggest the diagnosis of disease. Descending corticospinal fibers are responsible for the weakness and are the origin of the middle cerebellar peduncle MCP which projects to the intermediate zone of the cerebellum and then to the thalamus and cortex. Middle cerebellar peduncle cerebellum Inferior. The middle cerebellar peduncle MCP consists of the transversely coursing pontocerebellar fibers that arch across the midline and gather on each side 1. However both lesions had decreased signal abnormalities and were mildly smaller in size with the anterior pontine lesion measuring 113 x 10 mm and the middle cerebellar peduncle lesion measuring 10 x 7 mm Fig. Its origin from the contralateral pontine nuclei was first demonstrated by Vejas 1885 in.
Neuroimaging features and differential diagnoses. Cerbellar peduncle Vestibular Schwannoma acoustic neuroma. Its origin from the contralateral pontine nuclei was first demonstrated by Vejas 1885 in chronic experiments in the rabbit. Most of the lesions are demonstrated as hyperinten-sities on T2-weighted MR images and the signal intensity itself is nonspecific. Bilateral MCP lesions were most frequently observed in cerebrovascular diseases followed by neurodegenerative diseases inflammatory diseases toxic encephalopathies and lymphomas. Lesions limited to the bilateral middle cerebellar peduncles MCPs are uncommon.
Additional lesion found in the thoracic cord not shown and CSF led to the diagnosis of MS. Symmetrical lesions of the middle cerebellar peduncle. Lesions in the middle cerebellar peduncle include various pathological conditions ranging from infarction tumor infection trauma and demyelination to primary and secondary degeneration. MR imaging and differential diagnosis. Our findings demonstrate that bilateral MCP signal abnormalities are more common in patients. Characteristic distribution of lesions or involvement of specific anatomic sites however can suggest the diagnosis or narrow the differential diagnosis.
Arachnoid tissue of lower cranial nerves Posterior. Characteristic distribu-tion of lesions or involvement of specific anatomic sites however can suggest the diagnosis or narrow the differential diagnosis. Involvement of both middle cerebellar peduncles is uncommon but has a relatively long list of differential diagnoses including 1. Fragile X-associated tremorataxia syndrome. A cause of ataxic gait. Understanding the anatomy pathology imaging characteristics is important for the differential diagnosis of lesions in the middle cerebellar peduncle.
Bilateral middle cerebellar peduncle lesions. We describe common and less common diseases that can cause magnetic resonance signal abnormalities of middle cerebellar peduncles MCP offering a systematic approach correlating imaging findings with clinical clues and pathologic mechanisms. Multiple systemic atrophy MSA olivopontocerebellar atrophy. This retrospective study investigated diseases with a proclivity for the bilateral MCPs and explored the associations between their neuroimaging features and clinical findings for the differential diagnosis of such lesions. Petrous bone Superior. Neuroimaging features and differential diagnoses.
Myelin abnormalities different types of edema or neurodegenerative processes can cause areas of. Differential Diagnosis of Cerebellopontine Angle lesions. This retrospective study investigated diseases with a proclivity for the bilateral MCPs and explored the associations between their neuroimaging features and clinical findings for the differential diagnosis of such lesions. Fahr disease It is an uncommon familial neurodegenerative disorder which is characterized by abnormal cell loss and calcium deposition in basal ganglia mainly globus pallidus internal capsule dentate nucleus thalamus. This retrospective study investigated diseases with a proclivity for the bilateral MCPs and explored the associations between their neuroimaging features and clinical findings for the differential diagnosis of such lesions. The middle peduncle is purely afferent.
The middle peduncle is purely afferent. Objectives Lesions limited to the bilateral middle cerebellar peduncles MCPs are uncommon. Lesions limited to the bilateral middle cerebellar peduncles MCPs are uncommon. Differential diagnoses of middle cerebellar peduncle lesions in our patient included glioma malignant lymphoma or demyelinating diseases such as. Between their neuroimaging features and clinical findings for the differential diagnosis of such. Understanding the anatomy pathology imaging characteristics is important for the differential diagnosis of lesions in the middle cerebellar peduncle.
The purpose of this study was to investigate what diseases affect both middle cerebellar peduncles MCPs and to evaluate other MR features for differential diagnosis. Concourse 1_Concourse 2_Concourse. The middle cerebellar peduncle or the brachium pontis enters the cerebellum fairly laterally. Due to suspicion for demyelinating disease MRI of the spine and CSF analysis was recommended. Multiple systemic atrophy MSA olivopontocerebellar atrophy. Symmetrical bilateral lesions in middle cerebellar peduncles suggest fragile X ataxia syndrome.
Lesions in both the left anterior pons and the left middle cerebellar peduncle.
Hyperintensity Of The Middle Cerebellar Peduncles On Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery Imaging Variation With Age And Implications For The Diagnosis Of Multiple System Atrophy American Journal Of Neuroradiology

Pdf Mr Features Of Diseases Involving Bilateral Middle Cerebellar Peduncles Semantic Scholar
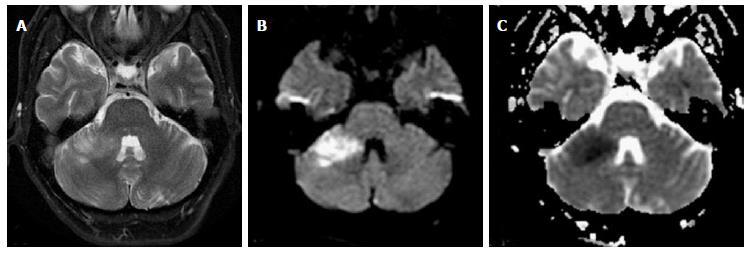
Middle Cerebellar Peduncles Magnetic Resonance Imaging And Pathophysiologic Correlate

Wallerian Degeneration In Middle Cerebellar Peduncles Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
T2 Weighted Mris Showed A Extended White Matter Lesions In The Middle Download Scientific Diagram
Mr Features Of Diseases Involving Bilateral Middle Cerebellar Peduncles American Journal Of Neuroradiology
Mr Features Of Diseases Involving Bilateral Middle Cerebellar Peduncles American Journal Of Neuroradiology
Mr Features Of Diseases Involving Bilateral Middle Cerebellar Peduncles American Journal Of Neuroradiology

Mri Brain Showing Revealed T2 Hyperintensities In Right Middle Download Scientific Diagram
Mr Features Of Diseases Involving Bilateral Middle Cerebellar Peduncles American Journal Of Neuroradiology

Ataxia And Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Lesions In Hepatic Encephalopathy Semantic Scholar
Hyperintensity Of The Middle Cerebellar Peduncles On Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery Imaging Variation With Age And Implications For The Diagnosis Of Multiple System Atrophy American Journal Of Neuroradiology


Posting Komentar untuk "Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Lesion Differential Diagnosis"